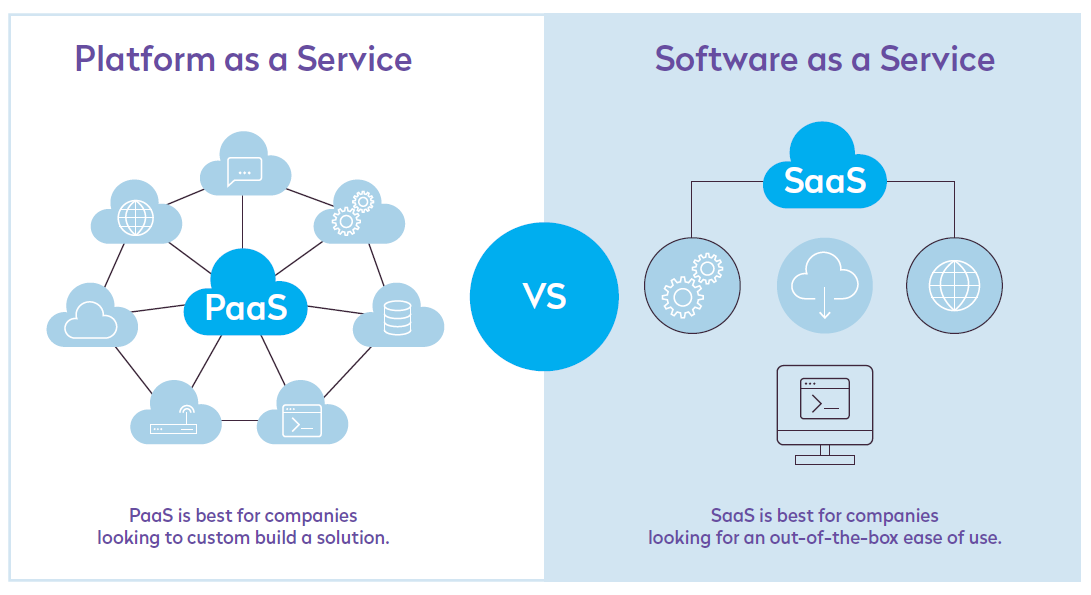
Software as a Service (SaaS) has become a cornerstone of the modern digital economy, revolutionizing how businesses operate and consumers access technology. From small startups to multinational corporations, SaaS solutions have empowered organizations with scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility. This article delves into the concept of SaaS, its benefits, challenges, and future potential, providing a comprehensive understanding of this transformative technology.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted on external servers and accessed by users over the internet. Unlike traditional software, which requires installation on individual devices, SaaS allows users to access the software through web browsers, enabling greater convenience and mobility.
Brief History of SaaS
The roots of SaaS trace back to the 1960s with the concept of time-sharing systems, where businesses accessed computing resources via a centralized mainframe. The term “SaaS” gained prominence in the late 1990s, thanks to pioneers like Salesforce, which introduced the first web-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform. Since then, SaaS has grown exponentially, driven by advancements in cloud computing and widespread internet adoption.
Key Features of SaaS
Several defining features set SaaS apart from traditional software models:
- Cloud Hosting: SaaS applications are hosted on cloud infrastructure, eliminating the need for local installation or complex hardware setups.
- Subscription-Based Pricing: SaaS solutions operate on a pay-as-you-go model, where users pay monthly or annually, reducing upfront costs.
- Accessibility: Users can access SaaS applications from any device with an internet connection, fostering flexibility and remote work.
- Automatic Updates: SaaS providers manage updates and maintenance, ensuring users always have access to the latest features.
How SaaS Works
At its core, SaaS leverages cloud computing to deliver software to end users. Here’s an overview of how it functions:
Architecture
SaaS applications typically use a multi-tenant architecture, where a single instance of the software serves multiple customers. This model optimizes resources and reduces costs for both providers and users. Alternatively, some SaaS providers offer single-tenant deployments, where each customer has a dedicated instance for enhanced security and customization.
Deployment Models
- Public SaaS: Applications are hosted on a shared infrastructure, accessible to multiple organizations.
- Private SaaS: Designed for specific organizations, offering greater control and security.
- Hybrid SaaS: Combines elements of public and private models to meet unique business needs.
Advantages of SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) has gained widespread adoption due to its numerous benefits:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Traditional software often requires significant upfront investments in licensing, hardware, and IT infrastructure. SaaS eliminates these costs, offering a subscription model that spreads expenses over time.
2. Scalability
SaaS platforms allow businesses to scale up or down based on their needs. Whether adding new users or integrating additional features, SaaS solutions can adapt seamlessly.
3. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
With SaaS, updates are handled by the provider, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches without manual intervention.
4. Flexibility and Accessibility
Users can access SaaS applications from any device with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote teams and on-the-go professionals.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
Many SaaS platforms are designed for teamwork, offering real-time collaboration features, file sharing, and communication tools that boost productivity.
Common Use Cases for SaaS
SaaS solutions are versatile, catering to a wide range of industries and functions. Here are some popular use cases:
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Platforms like Salesforce and HubSpot help businesses manage customer interactions, track leads, and analyze sales performance.
2. Collaboration Tools
Applications like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, regardless of location.
3. E-Commerce
Shopify and BigCommerce empower businesses to set up and manage online stores, offering tools for inventory management, payment processing, and marketing.
4. Data Analytics
SaaS platforms like Tableau and Looker provide advanced data visualization and analytics capabilities, helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
5. Marketing Automation
Tools like Mailchimp and Marketo streamline marketing efforts, enabling businesses to create, track, and optimize campaigns efficiently.
Challenges of SaaS
While SaaS offers numerous advantages, it is not without challenges.
1. Data Security Concerns
Since SaaS applications store data in the cloud, businesses must ensure robust security measures to protect sensitive information from breaches or unauthorized access.
2. Dependence on Internet Connectivity
SaaS applications rely on internet access, which can be a limitation in areas with unreliable connectivity.
3. Limited Customization
While SaaS platforms are designed for broad usability, they may lack the deep customization options offered by traditional software.
4. Vendor Lock-In
Switching providers can be challenging due to data migration complexities and reliance on specific SaaS ecosystems.
Emerging Trends in SaaS
The Software as a Service (SaaS) landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends shaping its future:
1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI-powered SaaS applications are becoming more prevalent, offering personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and automation.
2. Vertical SaaS Solutions
Unlike general-purpose platforms, vertical SaaS caters to specific industries, such as healthcare, finance, or education, offering tailored features.
3. Focus on User Experience
SaaS providers are prioritizing intuitive interfaces and seamless user experiences, enhancing adoption and retention rates.
4. Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms enable businesses to build and customize applications without extensive coding knowledge, democratizing software development.
SaaS vs. Traditional Software
The following table highlights the key differences between SaaS and traditional software:
| Aspect | SaaS | Traditional Software |
| Deployment | Cloud-based | On-premises |
| Payment Model | Subscription | One-time license fee |
| Maintenance | Handled by provider | Managed by user |
| Accessibility | Any device with internet | Limited to installed devices |
| Scalability | Easily scalable | Requires manual upgrades |
The Future of SaaS
The SaaS industry shows no signs of slowing down. According to recent reports, the global SaaS market is projected to exceed $400 billion by 2025.
Predictions
- Increased Adoption: More businesses, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), will transition to SaaS solutions.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Providers will focus on implementing advanced security protocols to address data privacy concerns.
- Integration with IoT: SaaS platforms will increasingly integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling new use cases.
- Sustainability Focus: As businesses prioritize environmental responsibility, SaaS providers will adopt green practices in their operations.
Challenges
Despite its growth, the SaaS industry must navigate challenges such as market saturation, evolving regulations, and rising competition.
Conclusion:
Software as a Service (SaaS) has transformed how businesses and individuals interact with technology, offering unparalleled convenience, scalability, and cost-efficiency. While challenges like security and vendor lock-in persist, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, making SaaS a vital component of the modern digital ecosystem.
As technology continues to evolve, SaaS will remain at the forefront, driving innovation and enabling businesses to thrive in an increasingly connected world. Whether you’re a startup looking for cost-effective solutions or a large enterprise aiming to enhance agility, SaaS offers a path to success in the digital age.